Gelatin is a gelling agent in packages like meals and pharmaceutical products. It is derived from animal connective tissues. These tissues are, on the whole, sourced from pigs and cows, even though gelatin can also be crafted from fish and bovine.
The production system includes extracting and purifying steps before being processed into the acquainted powdered or different products. One of the most attractive things about making gelatin is the ingenious reuse of normally expendable animal parts.
Also, many other types of cuisine, such as cakes and pastries, can benefit from the addition of gelatin's textural components and powerful gels due to its chemical composition. Another important function of this flexible component in pharmaceutical packaging is to encase therapeutic medications in a way. In this way, it makes them simpler to swallow. Knowing the ingredients and history of gelatin might help cooks better serve customers more concerned about sources.
Composition of Gelatin
Gelatin, a not unusual aspect utilized in an extensive style of foods, is derived from collagen, a structural protein observed inside the pores of the skin and bones of animals. Creating gelatin includes extracting collagen from those tissues with specific and gelling homes. This collagen is then broken into smaller products, ensuing inside the feature gelling homes that make gelatin beneficial in cooking, business packages, and meal manufacturing.
The composition of gelatin offers an important position in its functionalization. They offer crosslinking with other substances like Glycine, polymeric material, and amino acids. Gelatin possesses specific physiochemical, thermochemical, and emulsifying properties that gelatin manufacturers noticeably desire.
This useful ingredient with other materials like metal nanoparticles, minerals, and vitamins is used because of its unique desired properties in different cultures. Its modern and innovative applications in medicines, agricultural additives, and cosmetics complement its history of use in savoury dishes like aspics. It offers a focused chemical from the environment with a helpful concept to clean dessert detail.
Have you ever thought about the general mechanism for gelatin production? Gelatin is produced in connective tissues, skin, and bones of animals from collagen. However, agar-agar, vegetables, and fish may also transmit mechanical signals to close cells in gelatin composites and animal assets like beef gelatin.
Elevating demands for non-mammalian gelatin in food industries reinforced gelatin replacement from plant sources, such as pectin as a gelatin replacer. In this regard, mango peels are considered an ideal source with increased pectin for satisfying quality.
It helps to choose with ethical and dietary restrictions for the same gelling appealing to humans. Myriads of dietary products like marshmallows and dairy substances like yogurt and gummy candies show the importance of gelatin. In this way, consumption habits are improved in our meal systems.
As the era continues to increase and patron choices evolve, the destiny of gelatin manufacturing might also see innovation in the direction of sustainability and inclusivity for all consumers.

Sources of Gelatin
Gelatin can be sourced from different animals, including:
1.Bovine Gelatin :
Various meals and prescribed drugs have gelatin. It is a flexible substance derived from collagen.
Bovine gelatin is received by extracting collagen from cattle's connective tissues and bones. It entails boiling those animal elements to turn the collagen into gelatin. The ensuing product is subtle, similar to taking away impurities to make it subtle.
They have been developed recently because of nutritional regulations or moral worries surrounding animal products. Alternative to standard bovine-derived gelatin agar-agar is a plant-primarily based totally opinion. These plant-primarily based total options provide comparable binding and gelling properties, presenting an interesting prospect for the ones looking for non-animal-derived substitutes.
Creating gelatin involves prolonged heating of these animal byproducts to break the collagen into a more soluble form. This unique protein structure makes gelatin versatile in various food and non-food products.
Interestingly, gelatin manufacturing entails numerous steps to purify and refine the extracted collagen. Beyond the culinary realm, gelatin is used in pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, photography, or even a few clinical studies fields as a supply of protein because of its specific houses.
2. Fish gelatin
Gelatin is a flexible factor in many products, including the texture and shape of many foods. While conventional gelatin is derived from animal collagen, fish gelatin is another lesser-recognized supply.
This opportunity is appropriate for those who have cultural options or nutritional restrictions. These are acquired from the pores, skin, and scales of fish, which include tilapia or catfish; fish gelatin gives an interesting opportunity for those looking for a non-animal-primarily based option.
This shape of gelatine gives a precious protein supply while keeping gelling houses just like its animal-derived counterpart. Fish pores and skin are heated with water to launch collagen content. It is then accompanied with the aid of using filtration to put off impurities. Once purified, the ensuing liquid is dried and processed into the best powder. Fish gelatin's specific amino acid profile also helps pores, skin fitness, and joint function, supported by its perfect amino acid profile due to its herbal collagen content.
3. Pork gelatin
Gelatin is a generally used aspect in many meal merchandise. However, do you recognize what it is made of?
Pork gelatin , for example, is derived from the collagen in pig collagen pores, skin, and bones. This collagen is extracted in a manner that entails boiling the animal components to launch the protein. Once extracted, the collagen is purified and dried to shape the acquainted powdered gelatin we use in numerous medicinal merchandise and foods.
Interestingly, red meat gelatin has been used for hundreds of years due to its herbal gelling houses and capacity to offer texture and shape to numerous foods. However, knowing that a few humans may also avoid red meat-derived gelatin because of spiritual or nutritional restrictions is vital.
However, options including pork or fish-primarily based totally gelatins provide comparable purposeful houses for the ones looking for an opportunity source. There has been a developing hobby in plant-primarily based options to standard animal-derived gelatins. These substitutes offer comparable binding and gelling houses while catering to vegan and vegetarian nutritional preferences.
As purchaser attention around sourcing and manufacturing strategies keeps increasing, the meals enterprise has responded with a much wider variety of alternatives for incorporating gelatin-like houses into merchandise without animal-derived ingredients.

Gelatin Manufacturing Process
Gelatin is a flexible factor in many meal products, industries, pharmaceuticals, and cosmetics. It is crafted from animal skin, bones, and connective tissue collagen. The production method includes heating or boiling those uncooked substances to extract the collagen, which is then delicately processed into the gelatin.
Impact of Animal Source on Gelatin Properties
The form of animal used to supply gelatin can extensively affect its properties. For example, animal gelatin like beef or beef-primarily based gelatin has extraordinary strengths and textures compared to the ones crafted from fish or fowl assets. Furthermore, the purity of the collagen extracted and the way it's processed play a crucial role in figuring out the fine traits of the last gelatin substance.
Sustainable alternatives to gelatin
Sustainable options for gelatin As client choices continue to conform to extra sustainable and moral practices, there may be a developing hobby in opportunity reassets of gelatin, consisting of plant-primarily based totally or lab-grown options. These improvements should revolutionize the enterprise by supplying environmentally pleasant options and handing over overall performance and functionality.
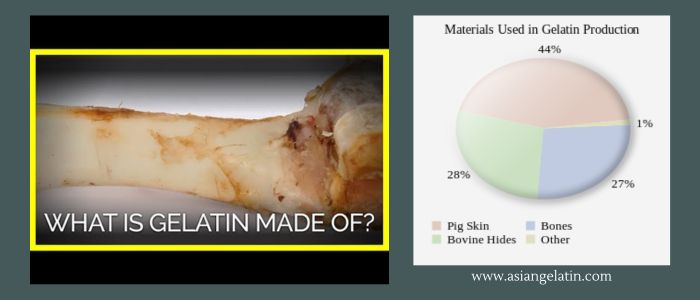
Gelatin, a multifaceted ingredient primarily sourced from pigskin, bovine hides, and fish scales, undergoes a myriad-step extraction process. Gelatin manufacturers utilize high-tech methods involving acid or base treatment to break down the collagen into its amino acids.
Comparisons between Gelatin Sources
A. Nutritional differences:
In the last decade, researchers have focused on studying valuable uses for varied species and improving the extraction of gelatin and collagen. As sources like cattle bones, pork, pig skin, bovine or beef hide, fish also affect people for nutritional restrictions. Also, nutritional compositions contribute to the specificity of gelatin.
Larger molecules of amino acids are a major source of a green supply of protein, which helps select particular cultural demands. For natural products, gelatin is imparting new uses like stabilizers, foaming agents, and eco-friendly materials because of its ability to form a gel, which is known traditionally.
Various health benefits are achieved, such as antihypertensive properties, antioxidant or anti-microbial properties, and the use of enzymes on gelatin or collagen to obtain bioactive substances.
B. Suitability for various industries:
As a biopolymer, gelatin is used in the food industry, pill formation, photography, meals, and drugs to improve stability, consistency, and elasticity. Protein-rich gelatin obtained after extraction, purification, and drying is set into sheets or powder to enhance texture. It is famous for its adhesive and thickening properties.
People are becoming aware of the origin of gelatin sources as the evolution of animal welfare is emerging. Researchers are becoming more interested in obtaining alternative synthetic sources for gelatin to fulfill consumers' demands for eco-friendly sustainability.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, Gelatin is renowned for its versatility and is made from different varieties of animal tissues. Varied varieties are obtained after gelatin extraction, purification, and drying. Owing to food texture, it is used in pharmaceuticals, photography, and cosmetics industries. Because of its specific composition, it is used in medicinal, business, and merchandise programs. It is all due to its capability to modify shape around energetic ingredients.
Post time: Dec-13-2023